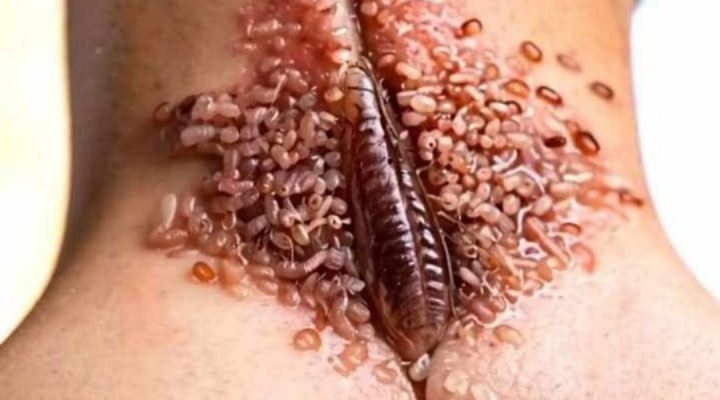
Cholinergic urticaria are heat-related hives that cause raised, red spots or an itchy rash. They can occur anywhere on the body (though the neck and chest are common) and typically lead to itching. They’re sometimes called heat bumps because they occur with heat-related sweating that’s caused by exercise, anxiety, or even spicy foods.1
There are several theories for why these hives occur, which are more common in males and people with allergies or skin conditions.2 They may actually be a type of allergic response to sweat. Diagnosis often means ruling out other causes, though the heat exposure (like a hot day or a hot bath) is often clear. Treatment will depend on the cause.
Symptoms
Cholinergic urticaria shares symptoms with other types of hives, such as a rash, but there can be differences. Cholinergic urticaria can include:2
- Raised bumps that are red or the color of your skin
- Itching where the hives occur, typically the neck and upper body
- Swelling (angioedema) at the site
- Generalized redness or discoloration, or mild swelling around the bumps.
In most cases, these heat-related hives go away in 15 minutes to a half-hour.1 However, some people experience recurring episodes.
“Urticaria” is the medical term for hives. Cholinergic urticaria is sometimes known as heat rash or heat hives. It will most often occur in males and people with a history of skin conditions like eczema. Symptoms typically emerge between ages 10 and 30.1
Like other forms of hives, cholinergic urticaria is believed to be caused by a malfunctioning autoimmune response. This response causes the immune system to attack healthy cells in the skin.
With cholinergic urticaria, this immune response is triggered by increased body temperature and sweating.3 This is known as a physical cause of hives (as opposed to an allergic cause).4 Research suggests that the neurotransmitter (chemical messenger) acetylcholine plays a role in this response.5
Increases in body temperature that cause cholinergic urticaria can be triggered by:1
- Exercise or physical exertion (the most common cause)
- Anxiety or emotional distress
- Stress
- Hot showers or baths
- Spicy foods
Diagnosis
If you experience one bout of cholinergic urticaria, you don’t need to seek diagnosis.6 But some people with the condition find that they develop chronic hives that can be difficult to get rid of.
A healthcare provider will:7
- Evaluate your symptoms and medical history
- Complete a physical exam
- Consider testing to try and isolate the cause6
Testing can include basic tests, like blood or urine tests, used to assess overall health and rule out another cause. Specific tests for cholinergic urticaria can include:8
- Skin testing with metal or glass cylinders used to apply heat or hot water baths
- Monitored exercise, which can help to rule out exercise-induced anaphylaxis (a separate diagnosis). This can involve a treadmill or stationary bicycle.
- Trials with injected acetylcholine to evaluate the response
Keeping a journal of when you experience hives and what may have caused them can help you get to a diagnosis.
If you experience cholinergic urticaria frequently or the condition begins to impact your quality of life, reach out to a board-certified dermatologist.
Treatment
Treatment for cholinergic urticaria focuses on avoiding triggers.9 For example, you may need to scale back intense exercise or skip hot baths. In addition, there are treatments for when hives strike and for controlling chronic hives:109
- Antihistamines, such as second-generation drugs like Allegra (fexofenadine) or Claritin (loratadine)
- Xolair (omalizumab), approved by the Food and Drug Administration for chronic cases
Some medications can be used off-label, meaning they’re approved for other uses but not directly for the condition. Ciclosporin, often used to treat eczema or psoriasis, is one such option.7
Some research has also shown that Dupixent (dupilumab), an injected medication used to treat eczema, may help with chronic hives.3 A steroid called danazol can improve chronic cholinergic urticaria.1 Other therapies reported in the literature can include:8
- Beta blockers, often used to treat high blood pressure, in combination with antihistamines and the asthma treatment Singulair (montelukast)
- Buscopan, an anticholinergic medication
- Botox injections
Some people have episodes of cholinergic urticaria but they don’t sweat, or they sweat very little. In these cases, therapy to induce sweating (such as hot baths or sauna use) may be helpful.11
Home Care and Prevention
Prevention focuses on avoiding triggers. If you experience a bout of cholinergic urticaria, you can try these home remedies for hives:
- Apply a cool compress.
- Wear loose clothing.
- Stay cool and reduce body temperature.
- Avoid scratching.
You also should avoid using alcohol, aspirin, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).7
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment with your healthcare provider if you have hives that don’t respond to treatment, or that cause swelling and pain.12 You should call 911 for immediate care if you experience signs of potentially life-threatening anaphylaxis, which can include:13